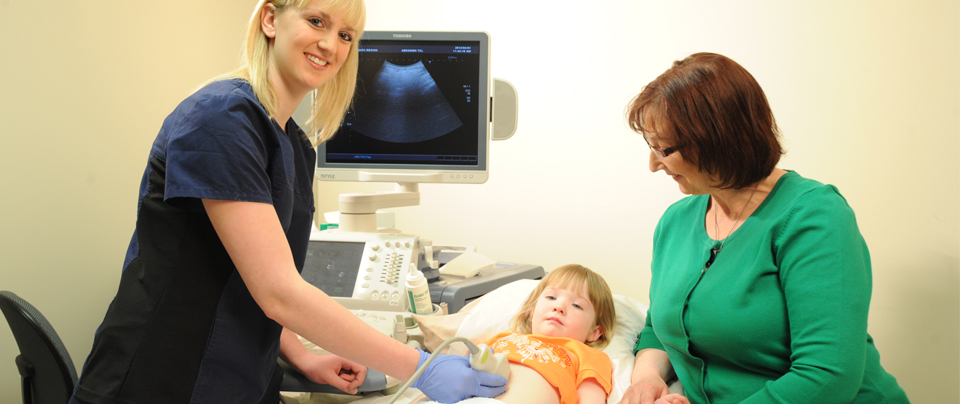
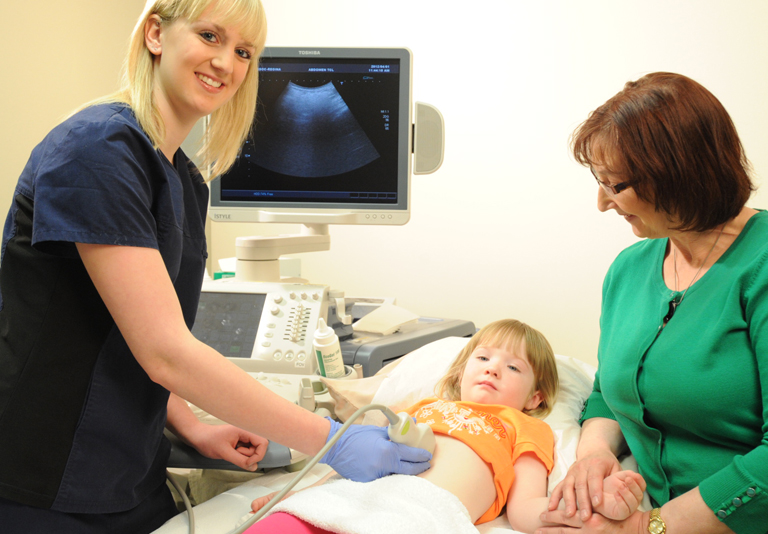
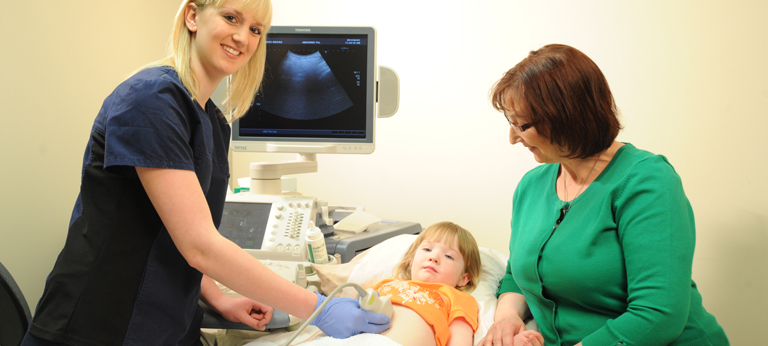
Ultrasound or sonography involves sending sound waves into the body. These sound waves reflect off the internal organs and are recorded by special instruments to create images of anatomic parts. No ionizing radiation (X-ray) is involved in ultrasound imaging.
Ultrasound images are captured in real-time so they can show movement of internal tissues and organs as well as the flow of blood in arteries and veins allowing physicians to assess normal and abnormal body function.
Ultrasound is also a non-invasive way of examining many of the body's internal organs, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, urinary bladder, uterus and ovaries.
One of the most common types of ultrasound is an obstetric ultrasound, which is the specialized use of sound waves to visualize and assess the development and growth of the embryo or fetus. The two dimensional (2D) images may be complemented by three dimensional (3D) ultrasound images to help evaluate many structures such as the uterus or fetal heart.
Benefits
- Ultrasound scanning is non-invasive and painless.
- Ultrasound is widely used.
- Ultrasound uses no ionizing (X-ray) radiation, making it an ideal modality for diagnosing and monitoring obstetric, gynecological and pediatric cases.
- Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, making it a good tool for guiding minimally invasive procedures.
- Ultrasound images can visualize structure, movement and document live function in the body's organs and blood vessels.
Risks
For standard diagnostic ultrasound there are no known harmful effects on humans.
Types of Ultrasound Exams We Perform
- Abdominal
- Female Pelvic
- Renal
- Scrotal
- Thyroid & Parathyroid
- Venous Vascular
- Breast
- Soft tissues (hernias, masses)
- Obstetrics
- 1st trimester and dating
- Nuchal translucency screening
- Anatomical survey
- Fetal growth
- Biophysical Profile and Doppler
- Cervical length and incompetence
- Placenta location
- C-Section scar assessment
- Pediatrics
- Abdomen
- Cranial
- Hips
- Spine
- Pyloric stenosis
- Musculoskeletal
- Shoulder
- Elbow
- Wrist
- Hand & Foot
- Ankle
- Hips
- Knees
Preparing for the procedure
Please review the Patient Preparation Sheet for your procedure, included in this section.
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for your ultrasound exam. Your doctor may instruct you not to eat or drink for as many as 12 hours before your appointment, though always consult the patient prep sheet for information. Clothing and jewelry in the area of your body that is to be examined will have to be removed.